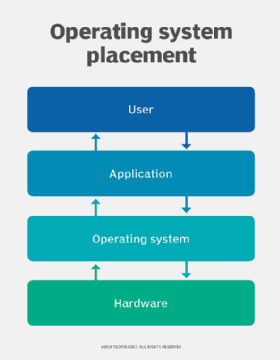
The process for a successful interview an Effective Job Interview
The process for a successful interview your collection contains the digital stack of curricula, with certain candidates moving the telephone screen. Next step: interviews with individuals. How can you use the relatively brief time to understand — and test — a near foreigner? How many people should participate in your company? What would you think if an applicant is a good fit for you? Finally, you have the right to ask questions like: “What is your main weakness?”
What the Experts Say
With the work market improving and applicants getting more possibilities, it is increasingly impossible to hire the right person for the job. Claudio Fernandez-Aaron, senior advisor for Egon Zehnder, the global executive search agency, writes It’s Not the How or What but the Who: Surceasing the Surrounding Yourself with the Best.
Interviews have been conducted on career web pages like Glassdoor,” says Sullivan, HR consultant, San Francisco State University Management Professor and author of 1,000 ways of recruiting top talent. twill turn its eyes to search other options if the interview phase of the organization, frightening candidates,” he says. Your duty is to evaluate applicants but also to persuade them to remain. Here is how you can work with — and with — the interview process.
The process for a successful interview Prepare your questions
You have to decide exactly what you are looking for in a prospective recruit before meeting applicants face to face, so that during the interview you are asking the correct question. Fernández-Aráoz recommends that the process be begun by “compiling an attribute list” for this position. Sullivan advises that you turn at the top performers for encouragement and advice. What do they have together? How resourceful are these? What have they done before they worked for your company? How did they play roles? These responses allow you to establish parameters and to formulate specific questions.
Reduce stress
The various unknowns lead applicants to find work interviews difficult. How’s my interviewer going to be? How is he going to ask questions? How do I cram my workday into this meeting? What do I wear, of course? He advises corrective measures to reduce the cortical levels of the applicant. Say in advance to people about the subjects they like to talk about so they can practice. You are prepared to meet the person at an appropriate time for him or her. Explain the dres’ code of the company. Your aim is to “make them happy” to make your interaction constructive and professional.
Assess potential
Fernández-Aráoz says that the budget for the first interview is two hours. This allows you “truly evaluate the skill and potential of the person.” Look for “curiosity, intuition, dedication, and resolve” indicators of the nominee. The question then becomes, can this person not only do the job now but in one year if the world has changed he or she can do the job?” Sullivan says: “None can forecast the future, but every day, you want someone to worry about it.”
Ask for real solutions
Don’t waste breath on irrelevant questions like What are the shortcomings? Try instead to discern how the candidate deals with the current working conditions. “How are you hiring a cook, after all? Cook you a meal for them,” he said. Identify a dilemma for the staff and ask the applicant if she can fix it. Or define the mechanism used by your organization and ask it to detect inefficiencies. Note, says Fernández-Aráoz, the preferred attribute list. When you are searching for a boss who would have to control several people over whom he does not have official authority.
The process for a successful interview Sell the job
If the meeting works fine and you think that the nominee is worth it, spend time selling the job and company during the second half of the interview. However, if the applicant has confidence, he advises “tell the person why they think he or she is fit.” Notice that an interview is a form of reciprocal screening. “Make it interesting,” Sullivan says. Ask them if they would like to know anyone on the squad. He states that the right candidates to market the work are those who “live it.” “Peers give the company an honest image.”