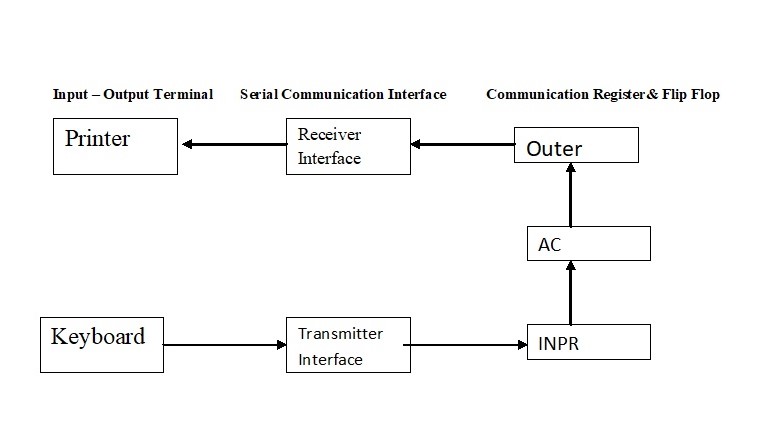
Vector Analysis
Vector analysis, a mathematics subject that deals with both size and direction quantities. The magnitude of some physical and geometrical values, termed scalars, can be completely specified in appropriate measuring units.
More and more weight, the temperature in grams and time in seconds can indicated on some scale. In certain numerical scales, scales can graphically represented as points, such as a clock or thermometer. There are other quantities that need direction and magnitude definition, termed vectors. Examples of vectors are speed, strength, and displacement. A vector quantity can graphically represented by an arrow pointing to the vector quantity, denoted by a directed line segment, which is the length of the segment expressing the vector magnitude.
Vector algebra.
A vector prototype is a guided section of the line AB (see Figure 1). It might considered that a particle would displaced from its original point A into a new position B. Vectors have usually referenced using boldface characters to distinguish from scalars.
More, in Figure 1, the vector AB can represented by a length (or size) |a|. In many cases, the location of a vector’s starting point has irrelevant. Such that two vectors have considered equal provided their length and direction have the same.
The equality of 2 vectors a and b has indicated by the conventional symbolic notation a = b and helpful definitions are provided by the geometry of the fundamental algebraic operations of a vector. More, if the movement from A to B of the particles has represented by AB=a in Figure 1.
Further More, the portion has then moved to a location C in the case of BC=b, then it has appeared that the movement from A to C may be carried out with a single AC = c movement. So the writing of a +b = c is reasonable.
A, B Vector
This structure of sum, c, a, and b is equally similar to the parallelogram Act in which diagonal ACs of the parallelogram built on the AB and AD vectors as sides produce the resulting c. Because the position of the vector beginning B B = b is irrelevant, BC = AD has followed. Figure 1 demonstrates the AD + DC = AC for switching legislation

Holds the added vector. Also, the association law is straightforward to illustrate.

The parenthesis in (2) has legal and can thus removed without ambiguities.
When s is scalar, sa is a vector with a length of |s||a| and the direction of which is positive in a when s and negative in contrast to that of a when s. A and an are, thus, vectors of identical size but opposite directions. The above definitions and the widely known characteristics of scalar numbers (as seen in s and t) indicate that.

Since legislation (1), (2), and (3) have similar laws in normal algebra. It has quite proper for systems with a linear equation containing a vector to solved by familiar algebraic rules. It enables many synthetic geometry theorems, which require complex geometrical structures, to derived by solely algebraic techniques.
Products of vectors.
The vector reproduction leads to two types of products, the dot product, and the cross product.
The dot or scale of two vectors a and b, written a·b, is a true number |a||b|cos (a,b), where (a,b) indicates an angle of a to b. Geometrically,

If a and B are in the right corner, a·b = 0, and if a b is not a zero vector, the vector is perpendicular to the disappearance of the dot product. When the square of a length has given a = b then cos (a,b) = 1, and a·a = |a|2.
For the dot multiplication of vectors, associative, commutative, distributive, and fundamental algebra rules apply.
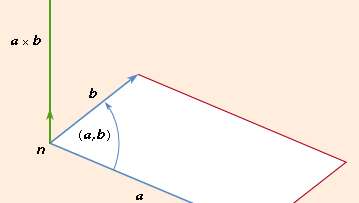
The vector of two vectors (a and b), abbreviated a stand b, is the cross- or vector product

where n is a unit length vector perpendicular to plane a and b and therefore a right-handed screw rotated from b to b moves towards n (see Figure 2). If a and b are parallel, then a = b is equal to 0. The size of the parallelogram with a and b as neighboring sides can equal the magnitude of paragraph b. Since the rotation between b and b is opposite,


This indicates that the product cross is not switchy, but the associative rule (sa) = B = s(a = b).

are valid for cross products.
Coordinate systems.
Given the lack of specific or accidental selections of reference frames established as physical relations and geometric configurations in the empirical laws of Physics, vector analysis is an appropriate research tool for the physical universe.
The introduction of a specific frame of reference or coordination system creates a correspondence of vectors and numbers that are the components of vectors in that frame and gives rise to certain operating rules for those numbers which follow the rules for the line segments.
If a particular set of three non-colinear vectors has picked, then every vector A may uniquely represented as a parallelepiped diagonal whose borders form part of A in the direction of the basis vectors. The axes of the famous Cartesian frame have guided by a set of three mutually orthogonal unit vectors (e.g. length vectors) 1 I j and k. (see Figure 3). The expression takes shape in this system.

where x, y, and z are the projections of A upon the coordinate axes. When two
vectors A1 and A2 have represented as the use of laws (3) yields for their
sum

Thus, in a Cartesian frame, the sum of A1 and A2 is the vector determined by (x1 + y1, x2 + y2, x3 + y3).
Also, the dot product can be written since
The use of the law (6) yields so that the cross product is the vector determined by the triple of numbers appearing as the coefficients of i, j, and k in