In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, businesses are constantly seeking solutions that strike a balance between the benefits of cloud computing and the security of on-premises infrastructure. Enter the hybrid cloud – a strategic blend of public and private clouds that allows organizations to harness the advantages of both worlds. In this article, we will explore the concept of hybrid cloud, its key characteristics, benefits, implementation strategies, and real-world examples of its transformative impact on businesses.
How does Hybrid Cloud works
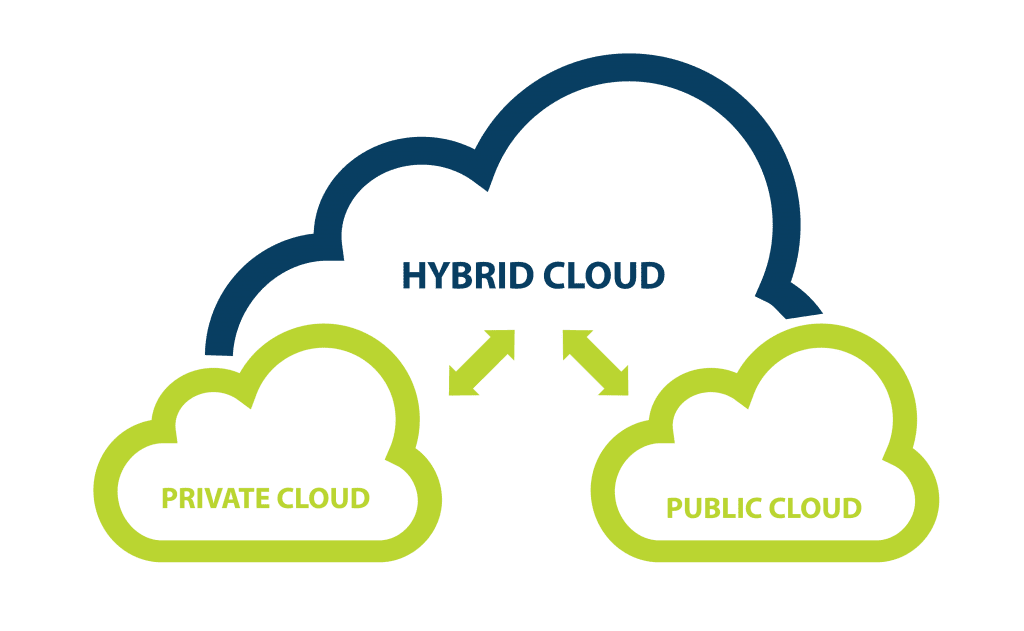
The hybrid cloud is a cloud computing model that combines the capabilities of both public and private clouds while allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This unique approach addresses the challenges that organizations face in terms of data security, compliance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Key Characteristics of Hybrid Cloud
- Integration: At the core of the hybrid cloud lies its ability to seamlessly integrate public and private cloud environments. This integration enables the movement of data and workloads between the two, based on specific business requirements.
- Data Portability: One of the defining features of hybrid cloud is the portability of data and applications. This flexibility allows organizations to choose where to host workloads based on factors such as performance, compliance, and cost.
- Scalability: Hybrid cloud solutions provide the scalability of public clouds alongside the control of private clouds. Organizations can scale resources up or down as needed, ensuring optimal performance without compromising security.
- Security and Compliance: Sensitive data and critical workloads can be kept within the confines of the private cloud, addressing security and compliance concerns. Non-sensitive workloads can be run on the public cloud for cost efficiency.
- Redundancy and Disaster Recovery: Hybrid clouds offer redundancy by allowing data to be stored on both public and private platforms. This redundancy enhances disaster recovery capabilities and ensures business continuity.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
- Optimized Performance: Hybrid cloud architecture allows organizations to run applications on the most suitable platform. Performance-intensive workloads can be run on the public cloud’s scalable infrastructure, while sensitive data can remain on-premises for security.
- Cost Efficiency: Hybrid clouds offer the advantage of cost optimization. Organizations can allocate resources efficiently, utilizing the public cloud for variable workloads and the private cloud for steady-state applications.
- Flexibility and Agility: The flexibility of hybrid cloud solutions enables rapid deployment of applications and services, reducing time-to-market for new initiatives. This agility is essential in today’s competitive landscape.
- Data Security and Compliance: Sensitive data can be kept within the secure confines of the private cloud, ensuring compliance with industry regulations while benefiting from the public cloud’s flexibility.
- Scalability and Resource Management: Hybrid cloud models provide businesses with the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing costs.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: The redundancy offered by hybrid clouds enhances disaster recovery capabilities. In the event of an outage in one environment, workloads can be shifted to the other for seamless business continuity.
Implementing a Hybrid Cloud Strategy
- Assessment and Planning: Begin with a comprehensive assessment of your existing infrastructure, identifying workloads suitable for migration to the public cloud and those that need to remain on-premises.
- Data Management: Determine how data will be managed and transferred between the public and private cloud environments. Implement strong data encryption and security protocols.
- Integration Solutions: Leverage integration solutions that facilitate communication and data flow between public and private clouds, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Management and Monitoring: Implement tools for centralized management and monitoring of the entire hybrid cloud environment. This enables efficient resource allocation and performance optimization.
- Testing and Optimization: Rigorously test the hybrid cloud setup to identify any issues or performance bottlenecks. Continuously monitor and optimize the environment for optimal performance.
Real-World Examples
- Netflix: The streaming giant utilizes a hybrid cloud model to deliver content to millions of users. It relies on Amazon Web Services (AWS) for its streaming needs while leveraging its own content delivery network (CDN) for improved performance and redundancy.
- NASA: NASA employs a hybrid cloud strategy to process and analyze the massive amounts of data generated by space missions. This approach combines public cloud resources for data analysis with on-premises infrastructure for data storage.
- Lululemon: The athletic apparel retailer adopted a hybrid cloud model to manage its e-commerce operations. It utilizes a public cloud for website hosting during peak shopping seasons while relying on a private cloud for sensitive customer data storage.
- Unilever: The consumer goods company employs a hybrid cloud approach to manage its global supply chain. It uses a combination of public and private clouds to optimize supply chain processes and enhance collaboration.
The hybrid cloud represents a powerful solution for organizations seeking to bridge the gap between the benefits of public and private cloud environments. By offering flexibility, scalability, security, and cost efficiency, hybrid cloud models empower businesses to make strategic decisions about data and application placement. As technology continues to evolve, the hybrid cloud will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of IT infrastructure, enabling businesses to thrive in the digital era by combining the best of both worlds.