Operation of Zener Diode
Zener Diode Perhaps the reverse voltage rises very quickly in the reverse current of a PN junction. This occurs as electrons have accelerated by the electrical field at the junction to high speeds and generate more free electrons by ionization of atoms. The field, therefore, speeds up these electrons, which induces further ionization. The mechanism of the avalanche leads to a huge current and the intersection has said to have broken down.
However, the disintegration is not harmful until the dissipation of power increases. The temperature to the degree where the local melting kills the semi-conductor. Over a broad spectrum of current, the voltage over the junction remains very stable. This effect has used to preserve the power supply output at the decommissioning voltage.
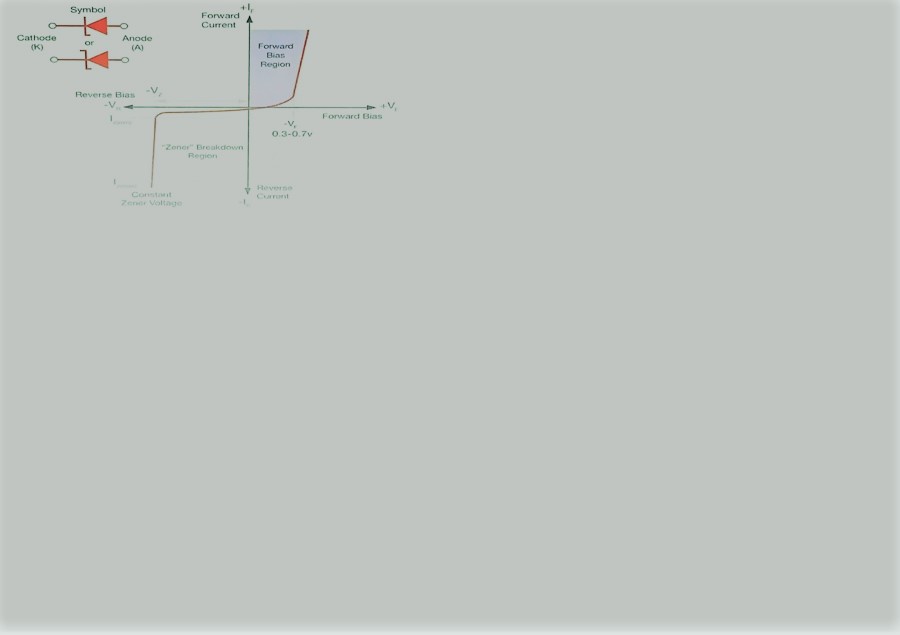
These PN junctions have referred to as the Zener diodes because of Clarence. Zener first proposed a reason for the sudden rise in current at collapse. Fig. 3-16 has a sharp transfer potential and a smooth current plateau above the breakdown. In the current-voltage curve of the Zener diode. Zener diodes can come from many milliamperes to several amperes with a decomposition voltage.
Figure 3-17 illustrates the way Zener diodes have used to regulate the output voltage of an electricity supply. The output voltage of the supplies shall not control exceed the diode’s zener-breakdown voltage. Then the potential increases to the potential for energy supply. If the load flow increases, the diode current decreases, so the reduction through Rs will still vary from the power supply voltage and the breakdown potential. The controlled output voltage remains constant at the diode breakdown potential, while the power-supply voltage changes under stress.
Zener Diode breakdown
The disintegration is either because of the effects of Zener under 5.5 V or because of ionization of the influence of more than 5.5 V. Both mechanisms lead to the same behavior and do not need any new circuitry, but the temperature coefficient of each mechanism is different.
The Zener impact has a low conductivity while the effect is positive. Both temperature effects are almost identical at 5,5 V and cancel each other such that the Zener diodes are the most stable under a large variety of environments at a rate of about 5,5 V.
Overvoltage protection
If the input voltage rises to a higher value than the Zener breakdown voltage, the current runs across the diode which causes a voltage drop through the resistor. The short circuit opens the fuse and separates the charge from the supply.
Clipping Circuits
AC waveform cutting circuits have used to alter or to form Zener diodes. The clipping circuit restricts or clips off portions of a waveform half or two cycles to shape the waveform.
Zener diode applications
Zener diodes are used as reference components, floating suppressors and in the device and cutting circuit switching for voltage control.