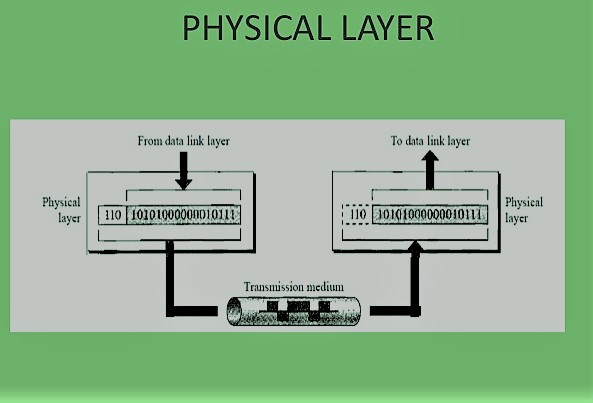
Physical Layer
Physical Layer is the only OSI network model layer that deals with two stations. The job of communicating with the real structure of hardware and signaling is to play the OSI model physical layer. This layer specifies the device, cables, cables, frequencies, pulses for binary signals, etc.
The physical layer offers the data-link layer facilities, Layer data links frames. The physical layer transforms them from a binary to an electric pulse. This has then transferred to binary information through wired or wireless media.
Signals
Before transmitting the data through a physical medium. It must first convert to electromagnetic signals. Data alone can be analogous to a human voice, or digital to a disc file. Analog and digital data have displayed either with digital or analog signals.
Digital Signals
The digital signals reflect a distinct existence and voltage pulse series. In the operating system circuits, digital signals have used.
Analog Signals
Analog signalling has in the form of a continuous wave which is expressed by electromagnetic waves.
Transmission Impairment
They appear to deteriorate as signals pass through the medium. There may be several reasons:
Attenuation of Physical Layer
The signal has to be high enough for the recipient to perceive the data correctly. The signal is weaker as it goes through the medium. It loses power by covering distance.
Dispersion
If the signal passes through the media. It continues to overlap and scatter. Depending on the used frequency, the sum of dispersion.
Delay distortion
Signals with predefined speed and frequency are transmitted over media. There are possibilities for signals that enter destinations arbitrarily where the signal speed and frequency do not match. This is really important in new media that certain bits hit faster than historically sent.
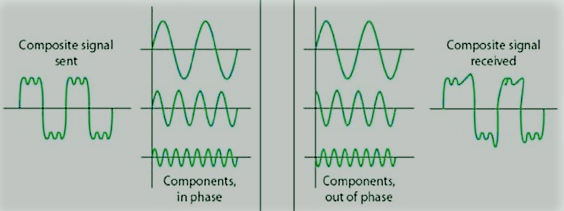
Noise of Physical Layer
Random analog or digital signal interference or variation is considered to be signal noise. Which could obscure the real data being transmitted. In one of the following classes, noise can be characterized.
Thermal Noise
Heat stirs a medium’s electrical conductors and can inject noise into the media. Thermal noise is inevitable to a certain extent.